부신 질환, Adrenal Diseases
|
부신의 생리학 |
|
|
|
원인 |
|
|
증상 징후 |
만성피로
|
|
진단 |
|
|
치료 |
|
■ 일차성(원발성) 부신 기능저하증 Primary Adrenal insufficiency
|
원인 |
|
|
증상 |
|
|
진단 |
|
|
치료 |
|
■ 급성 부신 기능 저하증 Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
|
원인
|
감염, 수술, 외상, 분만 또는 부신출혈 등으로 생길 수 있다. |
|
증상 및 징후 |
|
|
부신 위기 진단 및 치료 |
|
■ 2차성 부신 기능 저하증 Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency
|
■ 쿠싱 증후군 Cushing’s syndrome
|
원인 |
|
|
증상 징후 |
|
|
진단 |
|
|
치료 |
|
■ 부신 수질 질환
1. 크롬친화세포종 Pheochromocytoma
|
|
|
|
원인 |
|
|
증상 |
|
|
진단 |
|
|
치료 |
|
2. 원발성 알도스테론증 Primary aldosteronism .
|
원인 |
|
|
증상 |
|
|
진단 |
|
|
치료 |
|
■ 부신 우연종 Adrenal Incidentaloma
|
정의와 종류
|
|
|
증상 |
|
|
진단 |
|
|
치료 |
|
■ 내분비선의 구조와 호르몬의 기능 Anatomy of endocrine glands and Hormone function
사람 내분비 샘(내분비선)과 르몬의 종류와 기능
|
분비샘 |
호르몬의 명칭 |
동의어 |
약어 |
기능 |
|
시상하부 (Hypothalamus) |
부신피질 호르몬 자극 호르몬 (Corticotropin-releasing hormone) |
코르티코트로핀 분비호르몬– |
CRH |
ACTH을 방출시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
생식샘 자극호르몬 분비호르몬 (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) |
생식선 자극호르몬 분비호르몬 또는 황체호르몬 분비호르몬 (Lutenizing hormone releasing hormone, LHRH) |
GnRH |
뇌하수체 전 엽에서 LH와FSH를 방출시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
성장호르몬 분비 억제호르몬 (Growth hormone release inhibiting hormone) |
성장호르몬 억제호르몬 또는 소마토스타틴 (Somatostatin) |
GIH/SS |
뇌하수체 전 엽에서 성장호르몬 방출을 억제시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
성장호르몬 자극호르몬 (Growth hormone -releasing hormone) |
성장호르몬 방출 호르몬 |
GHRH |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 성장호르몬을 방출 시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
프로락틴분비억제호르몬 (Prolactin release -inhibiting hormone) |
프로락틴분비억제인자 |
PIH |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 프로랙틴 호르몬 방출을 억제시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
프로락틴 분비 촉진 인자 (Prolactin- releasing factor) |
프로락틴 분비 인자 |
PRF |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 프로랙틴 호르몬 방출시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
갑상샘 자극호르몬 분비 촉진호르몬 (Thyrotropin-releasing hormone) |
갑상선 자극호르몬분비호르몬 |
TRH |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 갑상선 호르몬을 방출시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
뇌하수체 전 엽 (Anterior pituitary gland) |
부신피질 자극호르몬 (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) |
코르티코트로핀 (Corticotropin) |
ACTH |
부신피질에서 부신피질 호르몬(코티솔, 안드로겐, 알토스테론)분비를 자극하는 기능을 한다. |
|
난포자극 호르몬 (Follicle-stimulating hormone) |
폴리트로핀 (Follitropin) |
FSH |
여성에서는 난소 난포 성장, 남성에서는 고환 세르톨리세포에서 정자 성장을 자극하는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
성장호르몬 (Growth hormone) |
소마토트로핀 (Somatotropin) |
GH/STH |
단백질을 합성하고 세포와 조직의 성장을 촉진 시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
황체형성 호르몬 (Lutenizing hormone) |
류트로핀 (Leutropin, interstitial cell stimulating hormone, ICSH) |
LH |
고환의 라이디히 세포에서 테스토스테론 분비, 난소의 황체성장을 자극해서 거기서 프로게스테론, 에스트로겐 분비를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
프로락틴 (Prolactin) |
젖 분비 호르몬– |
PRL |
여성 유방의 발달과 모유 생성을 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
갑상샘 자극 호르몬 (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) |
타이로트로핀 (Thyrotropin) |
TSH |
갑상성에서 갑상선 호르몬 T3, T4 을 합성과 분비를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
분비샘 |
호르몬의 명칭 |
동의어 |
약어 |
기능 |
|
뇌하수체 후 엽 (Posterior pituitary gland) |
항이뇨 호르몬 (Antidiuretic hormone) |
바소프레신 (Vasopressin) |
ADH |
혈관수축, 혈압상승을 시키는 작용이 있고 신장에서 수분흡수를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
옥시토신(Oxytocin) |
– |
OT |
여성의 유방에서 젖 유출을 촉진시키고 분만 중, 산후 자궁수축을 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
갑상샘(선) (Thyroid gland) |
칼시토닌(Calcitonin) |
– |
– |
뼈에 칼슘 침착을 촉진시키고 세포 외 칼슘 이온 농도 감소를 촉진시키는 작용을 한다. |
|
타이록신(Thyroxine) |
– |
T4 |
신체의 대부분의 세포에 화학작용을 일으켜 대사를 증진시킨다. |
|
|
트리아이오도타이로닌 (Triiodothyronine) |
– |
T3 |
||
|
부 갑상샘(선) (Parathyroid gland) |
부갑상샘 호르몬 (Parathyroid hormone) |
파라트호르몬 (Parathormone) |
PTH |
소화관과 신장에서 칼슘흡수를 증진시키고 뼈에서 칼슘유리를 증진 시켜서 혈중 칼슘이온 농도를 증가시킨다. |
|
부신 수질 (Adrenal medulla) |
에피네프린 (Epinephrine) |
아드레날린 (Adrenalin) |
EPI |
교감 신경 자극과 같다. |
|
노르에피네프린 (Norepinephrine) |
노르아드레날린 (Noradrenalin) |
NE |
||
|
부신 피질 (Adrenal cortex) |
알도스테론 (Aldosterone) |
– |
– |
신장에서 나트륨 재흡수, 칼륨분비와 수소이온 분비로 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
코르티솔(Cortisol) |
– |
– |
단백질.탄수화물.지방의 대사를 증진시키고 항염증 작용이 있다. |
|
|
췌장 (Pancreas) |
글루카곤(Glucagon) |
– |
– |
간에서 포도당을 만들어서 포도당을 체액 속으로 들어가게 된다. |
|
인슐린(Insulin) |
– |
– |
포도당이 세포 속으로 들어가게 작용하고 탄수화물 대사를 조절한다. |
|
|
소마토스타틴 (Somatostatin) |
– |
SS |
췌장 델타세포에서 분비되고 글루카곤과 인슐린의 분비를 억제해서 글루코스(혈당) 대사를 조절한다. |
|
|
고환 (Testes) |
테스토스테론(Testosterone) |
– |
– |
남성 생식기계 발달을 촉진 시키고 이차성징을 발육 시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
난소 (Ovaries) |
에스트로겐(Estrogens) |
에스트로젠 |
– |
여성 생식기계 발달을 촉진시키고 여성 유방과 여성 이차성징을 발육시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
프로게스테론 (Progesterone) |
– |
– |
여성 유방의 젖 분비관계를 발육시킨다. 수정난이 착상 할 수 있게 자궁내막을 조성한다. |
|
태반 (Placenta) |
사람 융모 생식샘 자극호르몬(Human chorionic gonadotropin) |
– |
HCG |
난소 황체 성장을 자극하고 그 황체에서 에스트로겐과 프로제스테론 분비를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
사람 몸 젖샘자극호르몬(Somatomammotropin) |
– |
– |
임신부 유방 발육을 자극 한다. 태아 성장을 자극한다. |
|
|
태반 에스트로젠 |
– |
– |
젖샘 발달 자극, 자궁 내막 발달과 유지, FSH, LH 분비 억제. |
|
|
태반 프로제스테론 |
– |
– |
모유 분비 관계 발달 자극 |
|
|
태반 락토겐(Placental lactogen) |
– |
– |
모유 생성 억제 |
|
|
신장 (Kidneys) |
레닌 (Renin) |
– |
– |
안지노텐시노겐을 안지노텐시노겐 I과 안지노텐시노겐 II로 변화 시키는 촉매 작용을 한다 |
|
적혈구 형 성 인자(Erythropoietin) |
– |
– |
적혈구 생성을 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
위 (Stomach) |
가스트린(Gastrin) |
|
|
위 벽 세포에서 위 염산 분비를 촉진 시키는 일을 한다. |
|
소장관 (Small intestine) |
세크리틴( Secretin) |
– |
– |
췌장을 자극해 췌장 분비자극을 한다. |
|
콜레시스토 키닌(Cholecytokinin) |
– |
CCK |
담낭을 수축 시키고 췌장 효소 분비를 자극한다. |
|
|
송과샘 (Pineal Glands) |
멜라토닌 (Melatoin) |
– |
– |
1일 주기 즉 밤낮 주기 조절 기능을 한다. 여성 월경 주기도 조절 한다. 남녀 성 충동에도 관여 한다. |
|
가슴샘 (Thymus gland) |
타이모신 (Thymosin) |
– |
– |
T 림프구 생성과 분화에 관여한다. |
뇌하수체에서
성장 호르몬,
갑상선 자극 호르몬,
부신피질 자극 호르몬,
난포 자극 호르몬(FSH),
황체형성 호르몬(LH),
프로락틴 호르몬이 분비되고 그로 인해 신체 기본 생명 유지가 계속되고 소아 성장 발육이 계속된다.
내분비선의 구조와 기능
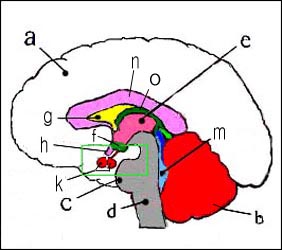
사진 1-1. 뇌하수체와 뇌 측면도.
a-대뇌, b-소뇌, c-뇌교(교뇌), d-연수(숨뇌), f-시상하부, g-간뇌, h-시신경 교차, k-뇌하수체의 전엽과 후엽, m- 제4뇌실, n-뇌량, o- 제 3뇌실.
참고 문헌-Grays anatomy
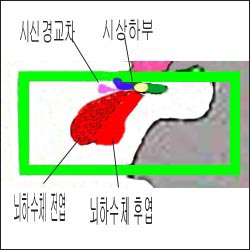
그림 1-2. 뇌하수체와 시상하부.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
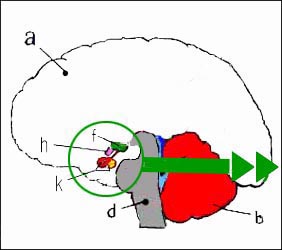
그림 1-3. 뇌하수체와 뇌 측면.
a-대뇌, b-소뇌, d-연수(숨뇌), f-시상하부, h-시신경 교차, k-뇌하수체 전엽과 후엽.
출처-Grays anatomy
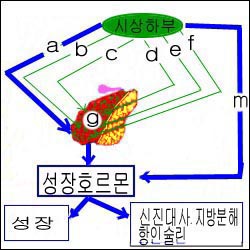
그림 1-4. 뇌하수체와 시상하부.
a-성장 호르몬 자극호르몬,
b-부신피질 자극호르몬,
c-갑상선 자극호르몬분비,
d-성샘 자극호르몬,
e-황체 자극호르몬 유리호르몬,
f-프로랙틴 자극인자와 프로랙틴 분비억제호르몬,
g-뇌하수체 전엽,
m-소마토스타틴(성장호르몬 분비억제 호르몬).
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
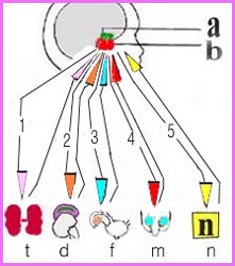
그림 1-6. 음성 피드백 기전(Negative feedback system)에 의해 뇌하수체와 신체 다른 계통에 있는 내분비선들과 상호 작용하여 호르몬 분비가 조절된다.
a-시상 하부, b-뇌하수체 전엽, d-부신, f-난소, m-고환, t-갑상선, n-심장·췌장·간장·신장·근육·지방·골격 등 각종계통과 기관,
1-갑상선 자극호르몬,
2-부신피질 자극호르몬(코르티코트로핀),
3-난포 자극호르몬(FSH),
4-난포자극호르몬(FSH),
5-성장 호르몬(소마토트로핀).
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.FAAP
- 뇌하체 후엽에서 항이뇨호르몬(ADH)과 옥시토신이 분비된다.
- 갑상선에서는 칼시토닌, 타이록신(T4), 트리아이오드타이로닌(T3)이 분비된다.
- 부갑상선에서 부갑상선 호르몬이 분비된다.
- 부신수질에서는 에피네프린과 노르에피네프린이 분비된다.
- 부신피질에서는 알도스테론과 코르티솔이 분비되고
- 췌장에서 글루카곤, 인슐린, 소마토스타틴이 분비된다.
- 고환에서 테스토스테론,
- 난소에서 에스트로겐과 프로게스테론이 분비된다.
- 뇌하수체와 신체의 각 계통에 있는 모든 표적 내분비선과 상호관계는 그림 1-6에서 볼 수 있다.
- 수요공급법칙과 음성 피드백 기전에 따라 뇌하수체에서 뇌하수체 자극 호르몬이 분비된다.
- 뇌하수체 내분비선 자극 호르몬의 영향으로 신체의 각 계통에 있는 각 표적 내분비선에서 특정 호르몬이 분비된다(빨간 선).
- 각 표적 내분비선 호르몬 분비 양의 증감에 따라, 즉 음성 피드백 기전에 따라 뇌하수체 자극 호르몬 분비 양의 증감이 생긴다(파란 선).
- 이와 같이 뇌하수체 자극 호르몬 분비의 양과 신체 다른 표적 내분비선 호르몬 분비의 양은 체내 호르몬 수요공급법칙과 음성 피드백 기전에 에 따라 변화되고 조절된다.
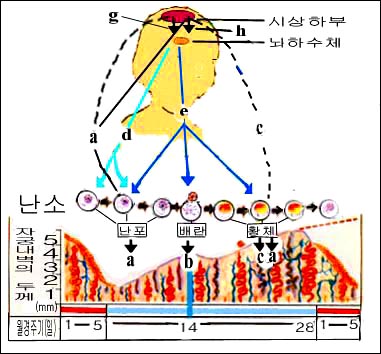
그림 1-7. 월경주기에 따른 여성 호르몬 분비 기전.
a-에스트로겐,
c-프로제스테론,
d-난포자극 호르몬,
e-황체형성 호르몬,
g-난포자극 호르몬 분비인자,
h-황체형성 호르몬 분비인자.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
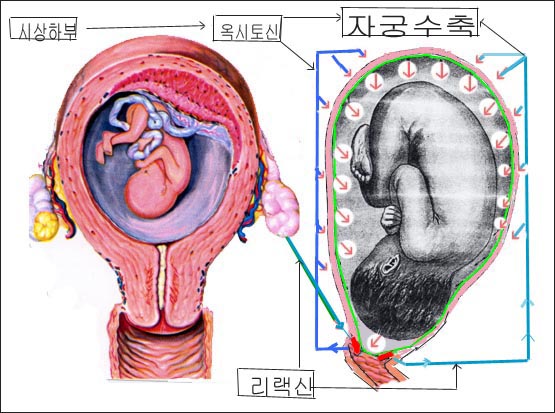
그림 1-8. 분만이 시작되면
- 자궁경관이 벌어지고
- 리랙신 호르몬이 난소의 황체에서 분비되고
- 그로 인해 자궁경관이 점점 더 벌어진다.
- 시상하부에서 뇌하수체 후엽 까지 연결시키는 특수 축삭이 있다.
- 시상하부에서 분비되는 신경 물질이 특수 축삭을 따라 뇌하수체 후엽으로 분비된다.
- 뇌하수체 후엽에서 옥시토신과 항이뇨 호르몬이 분비되고
- 옥시토신 작용으로 인해 자궁벽이 수축된다. (→ : 자궁 수축)
- Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
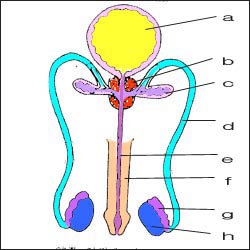
그림 1-9. 고환과 남성의 내부 생식기와 외부 생식기
a-방광, b-전립선, c-정낭, d-정관, e-요도, f-자지(음경), g-부고환, h-고환.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
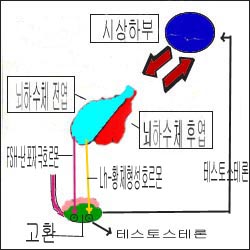
그림 1-10. 고환, 남성 호르몬-테스토스테론, 뇌하수체 호르몬.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 뇌하수체에서
-
- 성장 호르몬,
- 갑상선 자극 호르몬,
- 부신피질 자극 호르몬,
- 난포 자극 호르몬(FSH),
- 황체형성 호르몬(LH),
- 프로락틴 호르몬이 분비되고 그로 인해 신체 기본 생명 유지가 계속되고 소아 성장 발육이 계속된다.
- 인체 내분비선, 태반 호르몬, 임신 중, 분만 중, 분만 후 유방 발육과 모유 분비기전.
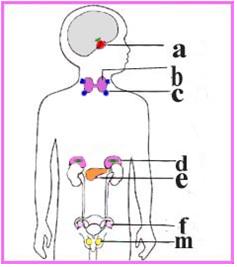
그림 1-34. 갑상선과 그 외 내분비선 해부도.
a-뇌하수체,
b- 갑상선,
c-부갑상선,
d-췌장,
e-부신,
f-난소,
m-고환 등은 내분비선들이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
인체 내분비선, 태반 호르몬, 임신 중, 분만 중, 분만 후 유방 발육과 모유 분비기전. 참조.
Adrenal Diseases
Physiology of the adrenal glands
• The adrenal glands are endocrine glands located above the left and right kidneys (kidneys).
• The adrenal gland is divided into cortex and medulla.
• Various steroid hormones such as cortisol, aldosterone and androgens are secreted by the adrenal cortex.
• Catecholamines such as norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine are secreted from the adrenal medulla.
• Adrenal hormone deficiency or excessive production can cause various diseases.
Cause
• Adrenal insufficiency is a disease caused by insufficient production of hormones in the adrenal cortex.
• It is classified into primary hypoadrenocorticism due to adrenal cortex disorder and secondary hypoadrenocorticism due to hypopituitarism.
• Causes of primary adrenal insufficiency include infection, cancer, bleeding, surgical removal, autoimmune disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and drug use.
• Secondary hypoadrenal insufficiency is the most common cause of steroid drug administration.
Symptoms, Signs
Chronic Fatigue
• lethargy;
• loss of appetite;
• weight loss;
• low blood pressure;
• Depression;
• Changes in skin or hair
• The skin turns black
• Brown spots around the mucous membranes of the mouth
• Adrenal insufficiency
• severe vomiting and abdominal pain; • low blood pressure;
• coma, etc.
Diagnosis
• Diagnosis is made with blood tests and, if necessary, CT and MRI of the adrenal gland and pituitary gland.
Treatment
• Treat according to the cause and treat with supplementation of insufficient hormones.
■ Primary Adrenal Insufficiency
Cause
• Adrenal insufficiency is a disease caused by insufficient production of hormones in the adrenal cortex.
• It is classified into primary hypoadrenocorticism caused by lesions of the adrenal cortex and secondary hypoadrenocorticism caused by hypofunction of the pituitary gland.
• Causes of primary adrenal insufficiency include infection, cancer, bleeding, surgical removal, autoimmune disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and drug use.
Symptoms
• Weakness and chronic fatigue
• lethargy;
• loss of appetite;
• weight loss;
• low blood pressure;
• depression,
• Changes in skin or hair
• Hyperpigmentation
• Brown spots around the mucous membranes of the mouth
• Adrenal insufficiency
• Vomiting, abdominal pain,
• Salt cravings
• coma
Diagnosis
• Diagnosis is made by medical history + symptom signs + examination findings + blood tests and abdominal CT imaging.
• Hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, anemia, nitrogen thrombosis, hypoglycemia, hypercalcemia, eosinophilia, and lymphocytosis may occur in primary adrenal insufficiency.
• Diagnosis by ACTH (Cortrosyn) stimulation test.
Treatment
• Treatment with glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, etc.
• Treat with insufficient hormone replacement.
■ Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
Cause
It can be caused by infection, surgery, trauma, delivery, or adrenal hemorrhage.
Symptoms and signs
• Symptoms, signs of adrenal insufficiency occur.
• Occasionally an adrenal crisis may occur and the following symptoms may occur. • low blood pressure;
• shock
• nausea, vomiting
• Exercise
• Heat
• Blood tests – hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, anemia, nitrogen thrombosis, hypoglycemia, hypercalciuria, eosinophilia, lymphocytosis, etc. may appear in primary adrenal insufficiency.
Diagnosis and treatment of adrenal crisis
• Diagnosis by ACTH (Cortrosyn) stimulation test.
• glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids,
• saline,
• Treatment of the cause;
• supportive care;
■ Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
• Blood tests show hyponatremia but not hyperkalemia;
• Hypotension is present but orthostatic hypotension does not occur. • Hypoglycemia is more common. • Hyperpigmentation occurs. • Minocorticoid function is preserved. • Diagnosis by ACTH (Cortrosyn) stimulation test. • Diagnosis is also made with the Insulin Hypoglycemia/Metyrapone/Low Dose Cortrosyn stimulation test.
■ Cushing’s syndrome
Causes
• Cushing’s syndrome is caused by prolonged exposure to cortisol. It is also called Hypercortisolism, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, or Hyperadrenocorticism.
• It may be caused by the following reasons.
• Adrenal hyperplasia
• Adrenal adenoma
• pituitary tumors;
• Ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting tumor;
• Iiatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome caused by drugs such as corticosteroids is relatively common.
• Excessive secretion of cortisol (cortisol/cortisol)
Symptoms Signs
• A round face like a full moon
• ‘buffalo neck
• Centrosome Obesity and Abdominal Obesity
• cleavage
• sexual dysfunction
• Amenorrhea or irregular menstruation;
• Osteoporosis, weak bones
• hirsutism,
• acne,
• High blood pressure,
• Type 2 diabetes;
• depression ,
• Weak skin
• headache
• Fatigue,
etc.
Diagnosis
• medical history + symptoms signs + examination findings
• Blood and urine tests, including cortisol levels
• Pituitary and adrenal gland CT and MRI imaging
• Dexamethasone Inhibition Test Dexamethasone Inhibition Test
• Salivary Cortisol Test
• Fundus examination
• Diagnosis is made by scintigraphy.
Treatment
• Depending on the cause, it is treated with appropriate drugs, surgery, or surgery and drugs.
• Corticosteroid drug iatrogenic Cushun syndrome is treated with drug discontinuation.
• Cushing’s syndrome caused by adrenal adenoma or ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma is treated surgically. Treatment with Hydrocortisone or Prednisolone after surgery
• It is also treated with drugs such as Ketoconazole, Metyrapone, and Myfepristone.
■ adrenal medulla disease
1. Pheochromocytoma
Causes
• A pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor.
• These tumors arise from the adrenal medulla.
• Norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine are secreted from the tumor.
Symptoms
• This can cause a number of symptoms.
• Headache, sweating, tachycardia, high blood pressure, abdominal pain, back pain, increased intracranial pressure, malignant hypertension, pallor, orthostatic hypotension, constipation, insanity, blurred vision, weight loss, polyuria, Daum, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, etc. can occur
Diagnosis
• Diagnosis is made by examining medical history + symptom signs + examination findings and by-products of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine as well as these two hormones.
• 24-hour urine test
• blood test
• Diagnosis is made by imaging tests such as adrenal CT, MRI, MIBG, and PET.
Treatment
• Surgical removal of the tumor and treatment with antihypertensive drugs such as alpha and beta blockers.
2. Primary aldosteronism.
Cause
• This disease is also called Conn’s syndrome.
• It is a disease caused by excessive production of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex.
• Primary aldosteronism is caused by adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal adenoma, malignancy, or
• It may be caused by adrenal familial aldosteronism.
Symptoms
• Overproduction of the aldosterone hormone
• Increased sodium and lower potassium in the body.
• High blood pressure develops and
• Myocardial infarction, enlarged heart or heart failure • Hypokalemia due to increased excretion of potassium in the urine;
• Symptoms such as numbness in the limbs, muscle cramps, and myasthenia gravis may occur.
• Vision impairment, headache
• polyuria, renal insufficiency;
• Irregular beats may occur.
Diagnosis
• History + symptoms + examination findings + Aldosterone and Renin tests and other blood tests and abdominal CT are used to diagnose.
• Diagnosis is made by saline suppression test, ambulatory salt loading test, or fludrocortisone suppression test (Saline suppression test, ambulatory salt loading test, or fludrocortisone suppression test).
Treatment
• Treat according to the cause.
• Treatment of aldosterone-secreting adenoma is performed with surgery.
• Adrenal hyperplasia can be treated with drugs such as Spironolactone or Eplerenone.
• Treat symptomatically according to other symptoms. • Treat as needed with dexamethasone.
■ Adrenal Incidentaloma
definition and kind
• Adrenal tumors discovered by chance are called adrenal incidentalomas.
• Adrenal adenoma of adrenal cortex, adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal malignancy
• A pheochromocytoma or ganglion neuroma of the adrenal medulla
• metastatic cancer
• Lipoma
• Neurofibromas, hemangiomas, cysts. Hematoma, granuloma, leiomyoma, teratoma, pseudoadrenal mass • Adrenal incidentalomas are classified into nonfunctional adrenal incidentalomas and functional adrenal incidentalomas that secrete specific hormones. Symptoms
• It occurs differently depending on the type of each adrenal incidentaloma.
Diagnosis
• Diagnosis is based on medical history + symptom signs + examination findings + each type of adrenal incidentaloma. Treatment • Treatment depends on the type of each adrenal incidentaloma.
■ Anatomy of endocrine glands and Hormone function
■ 내분비선의 구조와 호르몬의 기능
사람 내분비 샘(내분비선)과 르몬의 종류와 기능 Types and functions of human endocrine glands (endocrine glands) and hormones
|
분비샘 glands |
호르몬의 명칭 name of hormone |
동의어 synonym |
약어 Abbreviation |
기능 function |
|
시상하부 (Hypothalamus) |
부신피질 호르몬 자극 호르몬 (Corticotropin-releasing hormone) |
코르티코트로핀 분비호르몬– Corticotropin-releasing hormone |
CRH |
ACTH을 방출시키는 기능을 한다.It functions to release ACTH. |
|
생식샘 자극호르몬 분비호르몬 (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) |
생식선 자극호르몬 분비호르몬 또는 황체호르몬 분비호르몬 (Lutenizing hormone releasing hormone, LHRH) |
GnRH |
뇌하수체 전 엽에서 LH와FSH를 방출시키는 기능을 한다. It functions to release LH and FSH from the anterior pituitary. |
|
|
성장호르몬 분비 억제호르몬 (Growth hormone release inhibiting hormone) |
성장호르몬 억제호르몬 또는 소마토스타틴 (Somatostatin) |
GIH/SS |
뇌하수체 전 엽에서 성장호르몬 방출을 억제시키는 기능을 한다.It inhibits the release of growth hormone from the anterior pituitary gland. |
|
|
성장호르몬 자극호르몬 (Growth hormone -releasing hormone) |
성장호르몬 방출 호르몬 |
GHRH |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 성장호르몬을 방출 시키는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
프로락틴분비억제호르몬 (Prolactin release -inhibiting hormone) |
프로락틴분비억제인자 Prolactin release -inhibiting hormone |
PIH |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 프로랙틴 호르몬 방출을 억제시키는 기능을 한다. It inhibits the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. |
|
|
프로락틴 분비 촉진 인자 (Prolactin- releasing factor) |
프로락틴 분비 인자Prolactin- releasing factor |
PRF |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 프로랙틴 호르몬 방출시키는 기능을 한다. It functions to release prolactin hormone from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. |
|
|
갑상샘 자극호르몬 분비 촉진호르몬 (Thyrotropin-releasing hormone) |
갑상선 자극호르몬분비호르몬 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone |
TRH |
뇌하체 전 엽에서 갑상선 호르몬을 방출시키는 기능을 한다. It functions to release thyroid hormones from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. |
|
|
뇌하수체 전 엽 (Anterior pituitary gland) |
부신피질 자극호르몬 (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) |
코르티코트로핀 (Corticotropin) |
ACTH |
부신피질에서 부신피질 호르몬(코티솔, 안드로겐, 알토스테론)분비를 자극하는 기능을 한다. It stimulates the secretion of corticosteroids (cortisol, androgens, aldosterone) from the adrenal cortex. |
|
난포자극 호르몬 (Follicle-stimulating hormone) |
폴리트로핀 (Follitropin) |
FSH |
여성에서는 난소 난포 성장, 남성에서는 고환 세르톨리세포에서 정자 성장을 자극하는 기능을 한다. |
|
|
성장호르몬 (Growth hormone) |
소마토트로핀 (Somatotropin) |
GH/STH |
단백질을 합성하고 세포와 조직의 성장을 촉진 시키는 기능을 한다.It functions to synthesize proteins and promote the growth of cells and tissues. |
|
|
황체형성 호르몬 (Luteinizing hormone) |
류트로핀 (Leutropin, interstitial cell-stimulating hormone, ICSH) |
LH |
고환의 라이디히 세포에서 테스토스테론 분비, 난소의 황체성장을 자극해서 거기서 프로게스테론, 에스트로겐 분비를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.It stimulates the secretion of testosterone from the Leedig cells of the testis and the growth of the corpus luteum of the ovary, and there it functions to promote the secretion of progesterone and estrogen. |
|
|
프로락틴 (Prolactin) |
젖 분비 호르몬-Prolactin |
PRL |
여성 유방의 발달과 모유 생성을 촉진시키는 기능을 한다. It promotes the development of female breasts and the production of milk. |
|
|
갑상샘 자극 호르몬 (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) |
타이로트로핀 (Thyrotropin) |
TSH |
갑상성에서 갑상선 호르몬 T3, T4 을 합성과 분비를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.It functions to promote the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland. |
| glands |
호르몬의 명칭 name of hormone
|
동의어 synonym
|
약어 Abbreviation 기능 function |
기능 function |
|
뇌하수체 후 엽 (Posterior pituitary gland) |
항이뇨 호르몬 (Antidiuretic hormone) |
바소프레신 (Vasopressin) |
ADH |
혈관수축, 혈압상승을 시키는 작용이 있고 신장에서 수분흡수를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.It has the effect of constricting blood vessels and increasing blood pressure, and has a function of promoting water absorption in the kidneys. |
|
옥시토신(Oxytocin) |
– |
OT |
여성의 유방에서 젖 유출을 촉진시키고 분만 중, 산후 자궁수축을 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.It promotes the outflow of milk from a woman’s breast and promotes uterine contractions during and after childbirth. |
|
|
갑상샘(선) (Thyroid gland) |
칼시토닌(Calcitonin) |
– |
– |
뼈에 칼슘 침착을 촉진시키고 세포 외 칼슘 이온 농도 감소를 촉진시키는 작용을 한다.It promotes calcium deposition in the bone and acts to decrease the concentration of extracellular calcium ions. |
|
타이록신(Thyroxine) |
– |
T4 |
신체의 대부분의 세포에 화학작용을 일으켜 대사를 증진시킨다. It promotes metabolism by causing chemical reactions in most cells of the body. |
|
|
트리아이오도타이로닌 (Triiodothyronine) |
– |
T3 |
||
|
부 갑상샘(선) (Parathyroid gland) |
부갑상샘 호르몬 (Parathyroid hormone) |
파라트호르몬 (Parathormone) |
PTH |
소화관과 신장에서 칼슘흡수를 증진시키고 뼈에서 칼슘유리를 증진 시켜서 혈중 칼슘이온 농도를 증가시킨다. It increases calcium absorption in the digestive tract and kidneys and increases calcium liberation in the bones, thereby increasing the concentration of calcium ions in the blood.
|
|
부신 수질 (Adrenal medulla) |
에피네프린 (Epinephrine) |
아드레날린 (Adrenalin) |
EPI |
교감 신경 자극과 같다.It is like sympathetic nerve stimulation. |
|
노르에피네프린 (Norepinephrine) |
노르아드레날린 (Noradrenalin) |
NE |
||
|
부신 피질 (Adrenal cortex) |
알도스테론 (Aldosterone) |
– |
– |
신장에서 나트륨 재흡수, 칼륨분비와 수소이온 분비로 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.The kidneys promote sodium reabsorption, potassium secretion, and hydrogen ion secretion. |
|
코르티솔(Cortisol) |
– |
– |
단백질.탄수화물.지방의 대사를 증진시키고 항염증 작용이 있다. It enhances the metabolism of protein, carbohydrate, and fat and has anti-inflammatory action. |
|
|
췌장 (Pancreas) |
글루카곤(Glucagon) |
– |
– |
간에서 포도당을 만들어서 포도당을 체액 속으로 들어가게 된다.Glucose is made in the liver and the glucose enters the body fluids. |
|
인슐린(Insulin) |
– |
– |
포도당이 세포 속으로 들어가게 작용하고 탄수화물 대사를 조절한다.Acts to move glucose into cells and regulates carbohydrate metabolism. |
|
|
소마토스타틴 (Somatostatin) |
– |
SS |
췌장 델타세포에서 분비되고 글루카곤과 인슐린의 분비를 억제해서 글루코스(혈당) 대사를 조절한다.It is secreted by pancreatic delta cells and regulates glucose (blood sugar) metabolism by inhibiting the secretion of glucagon and insulin. |
|
|
고환 (Testes) |
테스토스테론(Testosterone) |
– |
– |
남성 생식기계 발달을 촉진 시키고 이차성징을 발육 시키는 기능을 한다.It promotes the development of male reproductive system and functions to develop secondary sexual characteristics. |
|
난소 (Ovaries) |
에스트로겐(Estrogens) |
에스트로젠 Estrogens |
– |
여성 생식기계 발달을 촉진시키고 여성 유방과 여성 이차성징을 발육시키는 기능을 한다.It promotes the development of the female reproductive system and functions to develop female breasts and female secondary sexual characteristics. |
|
프로게스테론 (Progesterone) |
– |
– |
여성 유방의 젖 분비관계를 발육시킨다. 수정난이 착상 할 수 있게 자궁내막을 조성한다. Develops the lactation system of the female breast. Creates the endometrium for the fertilized egg to implant. |
|
태반 (Placenta) |
사람 융모 생식샘 자극호르몬(Human chorionic gonadotropin) |
– |
HCG |
난소 황체 성장을 자극하고 그 황체에서 에스트로겐과 프로제스테론 분비를 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.It stimulates the growth of the bovine corpus luteum and functions to promote the secretion of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum. |
|
사람 몸 젖샘자극호르몬(Somatomammotropin) |
– |
– |
임신부 유방 발육을 자극 한다. 태아 성장을 자극한다. Stimulates breast growth in pregnant women. stimulates fetal growth; |
|
|
태반 에스트로젠 placental estrogen |
– |
– |
젖샘 발달 자극, 자궁 내막 발달과 유지, FSH, LH 분비 억제.Stimulates mammary gland development, endometrium development and maintenance, and inhibition of FSH and LH secretion. |
|
|
태반 프로제스테론placental progesterone |
– |
– |
모유 분비 관계 발달 자극 Stimulates the development of the lactation relationship |
|
|
태반 락토겐(Placental lactogen) |
– |
– |
모유 생성 억제 suppression of milk production |
|
|
신장 (Kidneys) |
레닌 (Renin) |
– |
– |
안지노텐시노겐을 안지노텐시노겐 I과 안지노텐시노겐 II로 변화 시키는 촉매 작용을 한다. It catalyzes the conversion of angiotensinogen into anjinotensinogen I and anginotensinogen II. |
|
적혈구 형 성 인자(Erythropoietin) |
– |
– |
적혈구 생성을 촉진시키는 기능을 한다.It promotes the production of red blood cells. |
|
|
위 (Stomach) |
가스트린(Gastrin) |
|
|
위 벽 세포에서 위 염산 분비를 촉진 시키는 일을 한다.It promotes gastric hydrochloric acid secretion from gastric parietal cells. |
|
소장관 (Small intestine) |
세크리틴( Secretin) |
– |
– |
췌장을 자극해 췌장 분비자극을 한다. Stimulates the pancreas to stimulate pancreatic secretion. |
|
콜레시스토 키닌(Cholecytokinin) |
– |
CCK |
담낭을 수축 시키고 췌장 효소 분비를 자극한다.It constricts the gallbladder and stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes. |
|
|
송과샘 (Pineal Glands) |
멜라토닌 (Melatoin) |
– |
– |
1일 주기 즉 밤낮 주기 조절 기능을 한다. 여성 월경 주기도 조절 한다. 남녀 성 충동에도 관여 한다. It controls the daily cycle, that is, the day and night cycle. It also regulates the female menstrual cycle. It is also involved in the male and female sexual impulses. |
|
가슴샘 (Thymus gland) |
타이모신 (Thymosin) |
– |
– |
T 림프구 생성과 분화에 관여한다.It is involved in the production and differentiation of T lymphocytes. |
In the pituitary gland growth hormone,
thyroid stimulating hormone,
adrenocorticotropic hormone,
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH),
luteinizing hormone (LH), The hormone prolactin is secreted, thereby sustaining the body’s basic life support and continuing the growth and development of children.
The structure and function of the endocrine glands

Picture 1-1. Pituitary gland and brain side view. a – cerebrum, b – cerebellum, c – pons (ponyceps), d – medulla oblongata, f – hypothalamus, g – diencephalon, h – optic nerve junction, k – anterior and posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, m – fourth ventricle, n – corpus callosum, o – 3rd ventricle. References – Grays anatomy

Figure 1-2. pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-3. Pituitary gland and sides of the brain. a – cerebrum, b – cerebellum, d – medulla oblongata, f – hypothalamus, h – optic nerve junction, k – anterior and posterior pituitary. Source – Grays anatomy

Figure 1-4. pituitary gland and hypothalamus. a-growth hormone stimulating hormone, b-corticotropic hormone, c-thyroid-stimulating hormone secretion, d-gonadotropin, e-luteinizing hormone free hormone, f-prolactin-stimulating factor and prolactin secretion inhibitory hormone, g – anterior pituitary, m-somatostatin (growth hormone secretion inhibitory hormone). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-6. Hormone secretion is regulated by interaction with the pituitary gland and endocrine glands in other systems of the body by a negative feedback system. a- hypothalamus, b- anterior pituitary gland, d-adrenal gland, f-ovary, m-testis, t-thyroid, n-heart, pancreas, liver, kidney, muscle, fat, skeleton, etc. various systems and organs;
1- thyroid stimulating hormone,
2-corticotropic hormone (corticotropin),
3-follicle stimulating hormone (FSH),
4-follicle stimulating hormone (FSH),
5-growth hormone (somatotropin). Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
• Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin are secreted from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
• The thyroid gland secretes calcitonin, thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3). • Parathyroid hormone is secreted by the parathyroid gland.
• The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine.
• The adrenal cortex secretes aldosterone and cortisol.
• The pancreas secretes glucagon, insulin, and somatostatin. • Testosterone in the testicles,
• The ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone.
• The pituitary gland and all target endocrine glands in each system of the body and their interrelationships are shown in Figure 1-6.
• The pituitary-stimulating hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland according to the supply-demand law and negative feedback mechanism.
• Under the influence of pituitary endocrine-stimulating hormone, specific hormones are secreted by each target endocrine gland in each system in the body (red line).
• The amount of pituitary-stimulating hormone secretion is increased or decreased according to the increase or decrease in the amount of each target endocrine hormone secretion, that is, according to a negative feedback mechanism (blue line).
• As such, the amount of pituitary-stimulating hormone secretion and the secretion of other target endocrine gland hormones in the body are changed and regulated according to the hormone supply and demand law in the body and the negative feedback mechanism.

Figure 1-7. The mechanism of female hormone secretion according to the menstrual cycle. a – estrogen, c-progesterone, d-follicle stimulating hormone, e-luteinizing hormone, g-follicle-stimulating hormone secretion factor, h-luteinizing hormone-releasing factor. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-8. When labor begins
• The cervix is dilated
• The hormone relaxin is secreted by the corpus luteum and
• This causes the cervix to dilate more and more.
• There is a special axon that connects from the hypothalamus to the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. • Nerve substances secreted from the hypothalamus are secreted to the posterior pituitary along a special axon.
• Oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone are secreted by the posterior pituitary,
• The uterine wall contracts due to the action of oxytocin. (→ : uterine contraction)
• Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-9. Testicles and internal and external genitalia in men a – bladder, b – prostate, c – seminal vesicle, d – vas deferens, e – urethra, f – cock (penis), g – epididymis, h – testicle. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-10. Testicles, male hormones – testosterone, pituitary hormone. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• in the pituitary gland •
o growth hormone,
o Thyroid stimulating hormone, o adrenocorticotropic hormone,
o Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH),
o luteinizing hormone (LH), o The hormone prolactin is secreted, thereby sustaining the body’s basic life support and continuing the child’s growth and development.
• Human endocrine glands, placental hormones, and mechanisms of breast development and milk secretion during pregnancy, during and after delivery.

Figure 1-34. Thyroid and other endocrine glands anatomy. a – pituitary gland, b-thyroid, c – parathyroid gland, d – pancreas, e-adrenal, f – ovary, m-testis, etc. are endocrine glands. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Human endocrine glands, placental hormones, breast development and mechanisms of breast milk secretion during pregnancy, during and after delivery. Reference.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL, Endocrine CONTROVERSIES IN ADULT PRIMARY CARE PRACTICE MAY15~16 2015