성장 호르몬, Growth hormone
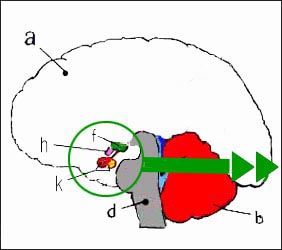
그림 1-41. 뇌하수체와 뇌 측면도.
a-대뇌, b-소뇌, d-연수(숨뇌), f-시상하부, h-시신경 교차, k-뇌하수체의 전엽과 후엽,
출처-Grays anatomy
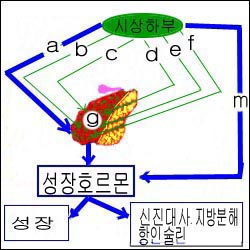
그림 1-42. 뇌하수체와 시상하부.
a-성장 호르몬 자극 호르몬, b-부신피질 호르몬 자극 호르몬, c-갑상선 호르몬 자극 분비 호르몬, d-성샘 자극호르몬, e-프로랙틴 자극 인자, f-프로랙틴 자극 인자, g-뇌하수체 전엽, m-소마토스타틴(성장 호르몬 분비 억제 호르몬).
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
- 뇌하수체는 신체의 전체 내분비선들을 컨트롤하는 내분비선 총 본부이다.
- 뇌하수체는 전엽과 후엽으로 나누어진다.
- 뇌하수체는 인간 기본 생명유지를 위한 생리를 총괄하고 조절한다.
시상하부 Hypothalamus
- 시상하부는
-
- 성장 호르몬 자극호르몬,
- 성장 호르몬 분비 억제 호르몬(소마토스타틴),
- 부신피질 호르몬 자극 호르몬,
- 갑상선 자극 호르몬 분비 호르몬,
- 생식샘 자극 호르몬 분비 호르몬(황체호르몬 분비 호르몬),
- 프로랙틴 분비 인자,
- 프로랙틴 분비 억제 호르몬을 분비한다.
- 시상하부에서 성장 호르몬 자극 호르몬과 성장 호르몬 분비억제 호르몬(소마토스타틴)이 분비된다.
- 시상 하부의 성장 호르몬 자극 호르몬과 소마토스타틴이 수요공급법칙과 음성 피드백 기전에 따라 성장에 필요한 정도의 호르몬 양이 분비되고 그 두 종류의 호르몬이 뇌하수체 전 엽을 자극해 뇌하수체 전 엽에서 성장 호르몬이 분비돼 소아청소년들이 정상적으로 성장발육하게 된다.
- 성장 호르몬은 육체적 운동이나 감정변화, 혈당의 농도 등 여러 가지의 인체 생리적 변화에 의해서 분비될 수 있다.
- 성장 호르몬은 도파민(dopamine)등 신경 전달물질이나 어떤 약물에 의해서도 분비될 수 있다.
- 시상하부에서 생성되는 소마토스타틴은 성장 호르몬 분비를 억제하는 작용을 한다.
성장 호르몬 기능
- 골단 연골을 자극해서 신장 성장을 촉진한다.
- 결제조직, 골, 근육, 피부, 내장 등이 비대 되게 한다.
- 인슐린에 대한 길항작용이 있다.
- 지방과 단백 신진대사에 영향 준다.
- 칼슘, 포타슘, 인, 소듐의 신진대사에 작용한다.
- 그 외
성장 호르몬 결핍의 원인
- 비특이성 뇌하수체 기능 저하증
- 종양, 외상, 감염, 염증, 기형, 조직구증, 방사선, 뇌하수체 기능 저하증 등 기질적 뇌하수체 손상과 병변
- 그 외
성장 호르몬 과잉의 원인
- 뇌하수체선 종양이 사춘기가 끝나기 전에 생기면 그로 인해 거인증이 생길 수 있고
- 사춘기가 끝난 후에 생기면 말단 거대증이 생길 수 있다.
소아 성장 호르몬 치료
- 소아 성장 호르몬 치료를 시작하기 전에 부모와 단골 소아과 의사, 주치의가 면밀한 상담을 해서 소아 성장 호르몬 치료 여부를 결정한다. 다음 경우, 성장 호르몬 치료를 할 수 있다고 (미 FDA)
-
- 성장 호르몬 결핍증
- 만성 신장 부전증
- 터너 증후군
- 프레이더 윌리 증후군
- 자궁 내 성장지연
- 임신 주 수에 비해 저 체중 신생아
- 특발성 저 신장
- 누난 증후군
- 그 외
소아 성장 호르몬 치료의 부작용
- 갑상선 기능 저하증,
- 양성 두개강 내 고혈압,
- 사춘기 전 유방 비대증,
- 당뇨성 망막증,
- 이미 있던 척추 측만곡증의 악화,
- 관절통,
- 근육통,
- 두통,
- 부종,
- 췌장염,
- 신체 체액증가,
- 주사 맞은 부위 피부발진이 생길 수 있고 지방 증가증도 생길 수 있다.
- 피부색소 침착증 등이 생길 수 있다.
- 알레르기 반응
Growth hormone

Figure 1-41. Pituitary gland and brain side view. a – cerebrum, b – cerebellum, d – medulla oblongata, f – hypothalamus, h – optic nerve junction, k – anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland, Source – Grays anatomy

Figure 1-42. pituitary gland and hypothalamus. a-growth hormone-stimulating hormone, b-corticotropin-stimulating hormone, c-thyroid-stimulating-releasing hormone, d-gonadotropin, e-prolactin-stimulating factor, f-prolactin-stimulating factor, g-anterior pituitary, m- Somatostatin (a hormone that inhibits the secretion of growth hormone). Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• The pituitary gland is the headquarters of the endocrine glands that control all endocrine glands in the body.
• The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior lobe and a posterior lobe.
• The pituitary gland oversees and regulates the physiology for basic human life.
Hypothalamus
• The hypothalamus
• o growth hormone stimulating hormone,
o Growth hormone secretion inhibitory hormone (somatostatin),
o corticosteroid stimulating hormone,
o thyroid-stimulating hormone-releasing hormone,
o gonadotropin-releasing hormone (progesterone-releasing hormone);
o prolactin secreting factor,
o Secretes prolactin secretion inhibitory hormone.
o The hypothalamus secretes growth hormone stimulating hormone and growth hormone secretion inhibitory hormone (somatostatin).
• Growth hormone-stimulating hormone and somatostatin in the hypothalamus secrete the amount of hormone required for growth according to the supply-demand law and negative feedback mechanism. This allows children and adolescents to grow and develop normally.
• Growth hormone can be secreted by various physiological changes such as physical exercise, emotional changes, and blood sugar concentration.
• Growth hormone can be secreted by any drug or neurotransmitter such as dopamine.
• Somatostatin produced by the hypothalamus acts to suppress the secretion of growth hormone.
Growth hormone function
• Stimulates epiphyseal cartilage to promote kidney growth.
• It causes the payment tissue, bone, muscle, skin, and internal organs to be enlarged.
• It has an antagonistic action on insulin.
• Affects fat and protein metabolism.
• Acts on the metabolism of calcium, potassium, phosphorus and sodium.
• etc
Causes of Growth Hormone Deficiency
• Nonspecific hypopituitarism
• Injuries and lesions of the organic pituitary gland, such as tumors, trauma, infection, inflammation, malformations, histiocytosis, radiation, and hypopituitarism
• etc
Causes of excess growth hormone
• If a pituitary gland tumor develops before the end of puberty, it can result in gigantism.
• After puberty, acromegaly can occur.
Pediatric Growth Hormone Therapy
• Before starting pediatric growth hormone therapy, parents, regular pediatricians, and primary care physicians should consult closely to decide whether or not to treat pediatric growth hormone. Growth hormone therapy can be used in the following cases (US FDA)
• o Growth hormone deficiency o Chronic kidney failure o Turner syndrome o Prader-Willi Syndrome o Intrauterine growth retardation o Low weight newborns for the number of weeks of gestation
o Idiopathic short stature
o Noonan syndrome
o others
Side effects of pediatric growth hormone therapy
• hypothyroidism;
• benign intracranial hypertension,
• Breast enlargement before puberty;
• diabetic retinopathy;
• exacerbation of pre-existing scoliosis;
• joint pain;
• Muscle pain,
• headache,
• edema;
• Pancreatitis;
• increased body fluids;
• You may develop a skin rash at the injection site and you may also develop lipomas.
• Skin pigmentation may occur.
• Allergic reactions
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.